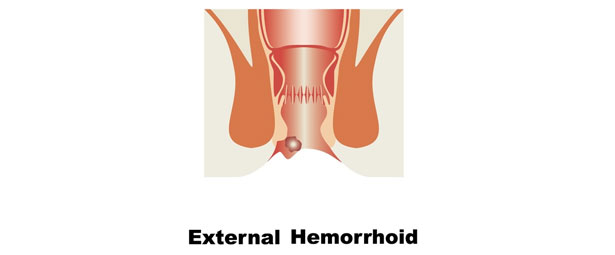
About three out of four adults will develop at least one external hemorrhoid in their life.
Hemorrhoids are best described as swollen veins in the lower rectum and anus. External hemorrhoids are visible without having to insert a scope into the anus. These are generally located around the anus.
- There are multiple causes, but in many cases, the exact cause is not identified.
- Pregnancy causing increased pressure on the veins in this area and straining when trying to have a bowel movement are common reasons for hemorrhoids.
Symptoms
When someone has a hemorrhoid, there are several symptoms that may occur, including:
- Bleeding during bowel movements that does not cause pain. This is usually noticed when the patient sees bright red blood either in the toilet or on the tissue after a bowel movement
- Discomfort or pain
- Anal region irritation or itching
- Swelling in the area surrounding the anus
- A lump located close to the anus, that can be either painful or sensitive
External hemorrhoids can bleed or itch when they are irritated. This may occur if the patient sits for a prolonged period of time or if they wear clothes that constantly rub the hemorrhoid.
With an external hemorrhoid, there are times when blood is able to pool in it. This can eventually clot and when this happens, it is referred to as a thrombosed hemorrhoid. When this occurs, patients may experience swelling, a hard lump, severe pain and inflammation.


Treatment
In most cases, an external hemorrhoid can be diagnosed simply by the doctor looking at it. Over-the-counter hemorrhoid medications are often recommended when it is mild and not causing severely bothersome symptoms. There are various ointments, pads, creams, and suppositories that contain ingredients, such as hydrocortisone, witch hazel, and lidocaine. The purpose of these is to alleviate itching and pain. They should be used exactly as directed.
Certain lifestyle remedies are also often recommended for minor to mild hemorrhoids. These may include:
- Eating foods high in fiber to reduce the risk of constipation and having to strain to have a bowel movement
- Soaking in a sitz bath
- Using moist toilet tissue or towelettes
- Over-the-counter oral pain relievers
- Ensuring the anal area remains clean with gentle cleaners that are alcohol-free
- Using cold packs to alleviate swelling
When conservative measures are not enough, minimally invasive procedures might be necessary. These may include a thrombectomy for hemorrhoids that have a blood clot, or shrinking external hemorrhoids using injected chemical solutions, rubber band ligation, or coagulation. For hemorrhoids that are especially large or resistant to treatment, patients might consider surgical options, such as hemorrhoid stapling or removal.
External hemorrhoids are relatively common, especially among those age 50 and older. If patients have a hemorrhoid that is bothersome, they should not hesitate to make an appointment with their doctor.