
Hiatal hernias are focused around the hiatus, which is an opening in the diaphragm.
When the body experiences an internal part or organ pushing through the cavity that contains it, this is referred to as a hernia. There are a number of different types of hernias that a person may experience. Among these is a hiatal hernia.
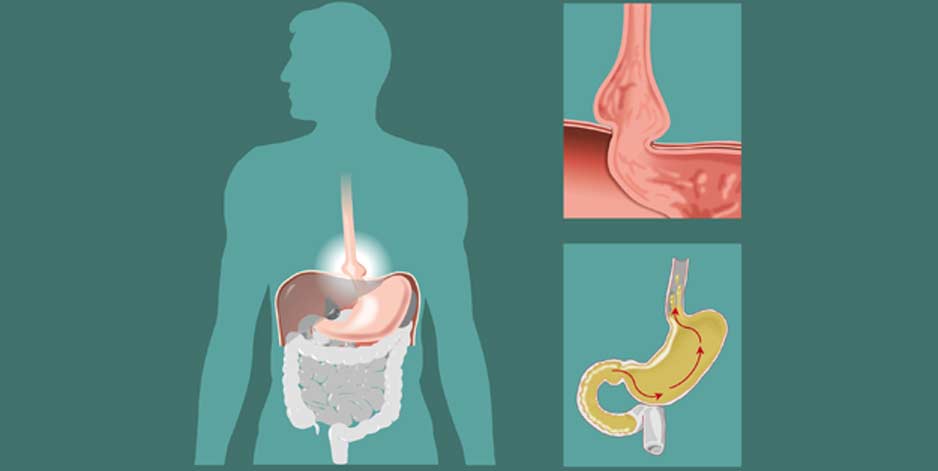
The hiatus opening allows the food pathways to pass through the diaphragm and attach to the stomach. The diaphragm provides a barrier separating the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity. When a hiatal hernia occurs, the stomach which resides in the abdomen pushes up through the hiatus.
Types of Hiatal Hernias
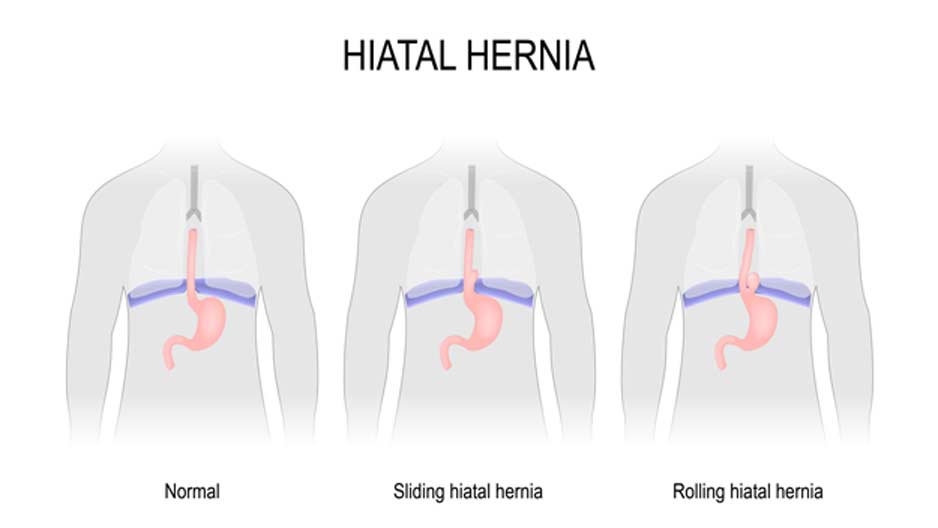
There are two types of hiatal hernia to be aware of: sliding and para-esophageal. The more common of the two is the sliding. When this type of hiatal hernia occurs, it is the stomach and the portion of the esophagus that attaches to the stomach that bulges into the chest cavity.
The occurrence of a para-esophageal hiatal hernia is a bit more serious. With this type of hiatal hernia, only a portion of the stomach bulges through the hiatus and rests next to the esophagus. The danger stems from the possibility that the blood supply to the stomach may be strangled and cut off.
Possible Symptoms & Causes
For many of the patients that have a hiatal hernia, there are no symptoms. Others, however, may experience heartburn that stems from gastroesophageal reflux, or what is also known as GERD. Chest pain often follows comes in conjunction with the heartburn.
There is no definitive cause for a hiatal hernia, and in most instances the cause is unknown. There are some factors, however, that may contribute to its occurrence. These include being born with a large hiatus, as well as an increase of pressure in the abdomen due to pregnancy, obesity, and the strain from bowel movements. Risk factors include being overweight and being over 50 years of age. Females are also at an increased risk.
Diagnosis & Treatment
To accurately diagnose a hiatal hernia, physicians will use an X-ray that is specialized for this procedure. A barium swallow is used to illuminate the esophagus so that it can be seen and examined. Another method to diagnose a hiatal hernia is by performing an endoscopy.
Once it is determined that a patient has a hiatal hernia, there are a few options for treatment. For the vast majority of patients, there won't be any symptoms and therefore there won't be any need for treatment. For those who suffer from symptoms of GERD, such as heartburn, the symptom rather than the hernia itself should be treated. The more serious type of hiatal hernia involves strangulation of the stomach and the loss of blood. When this occurs, active treatment in the form of surgery should take place to repair the hernia. This is typically a minimally evasive procedure that utilizes laparoscopic surgery.
