Some hemorrhoids go away on their own within a few days, but others may require medical treatment.
What are Hemorrhoids?
Hemorrhoids are inflamed or swollen veins in the lower rectum and anus. Hemorrhoids can be aggravated by:
- Straining during bowel movement
- Sitting for long periods of time
- Constipation
- Frequent diarrhea
- Overuse of laxatives
- Poor diet
- Pregnancy
- Genetic predisposition
- Infection of the rectum
The two types of hemorrhoids are external and internal. External hemorrhoids are located under the skin of the anus and cause itching, pain, and (in some instances) bleeding. Internal hemorrhoids are found inside the anus and eventually pass through and become external hemorrhoids.

How Long Do Hemorrhoids Last?
There isn’t a clear answer to this question. Some patients feel better within a few weeks, while others may need surgery.
Small internal or external hemorrhoids may heal within a week, while larger internal hemorrhoids may last a few months.
Patients experiencing hemorrhoids for the first time may recover faster than patients with recurrent hemorrhoids.
At-Home Treatment For Hemorrhoids
Some patients have recurring hemorrhoids due to weakened supporting tissue in the rectum and anus. To help manage hemorrhoids, patients should:
- Eat high-fiber foods, such as green vegetables and fruits
- Drink lots of water
- Avoid coffee and alcoholic beverages
- Take a fiber supplement or gentle stool softener
- Take warm bath with Epsom salt or sit in a tub with a few inches of warm water at least three times a day for 20 minutes
- Apply over-the-counter hemorrhoid creams
- Stay active and exercise regularly to improve blood circulation and prevent constipation
Patients should avoid straining during a bowel movement, as this can make hemorrhoids worse.
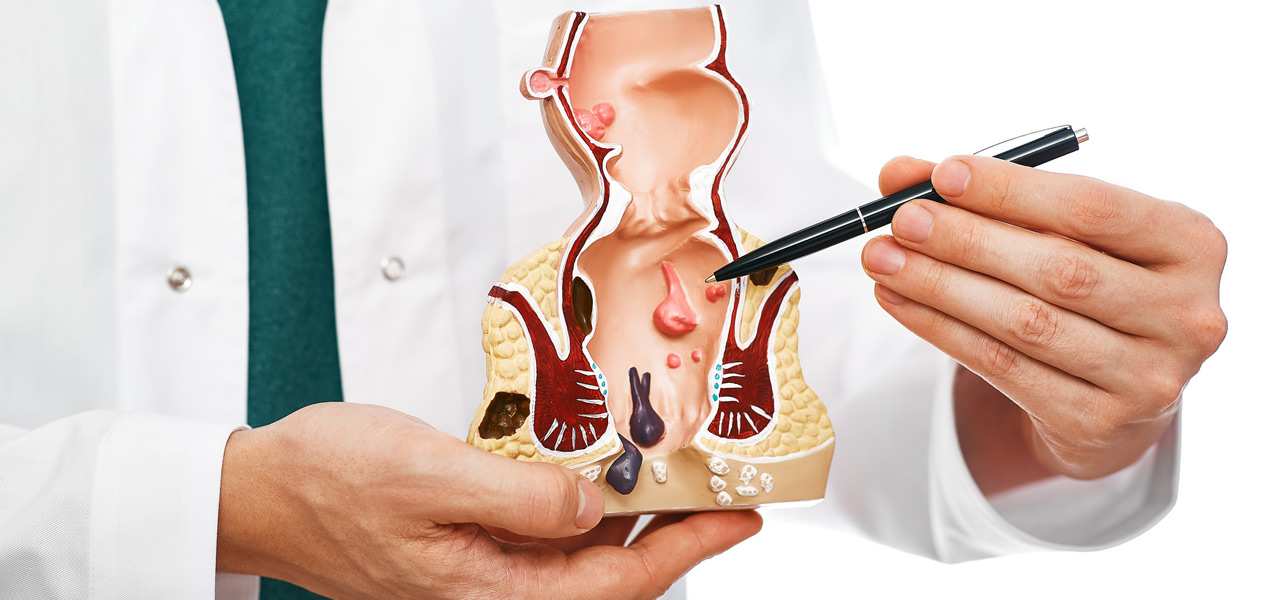
Medical Treatment For Hemorrhoids
Patients may need medical attention if one week of at-home remedies fail to provide relief. Rectal bleeding is another sign that patients need medical attention. Patients experiencing severe pain, bleeding, fever, and abdominal pain should seek medical care immediately.
During a medical appointment, the physician will rule out other potential causes of bleeding, such as Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, and cancer. The physician will perform a visual exam for external hemorrhoids, but internal hemorrhoids will be evaluated using a digital rectal exam or anoscopy.
Patients may be advised to use over-the-counter creams or ointments. Severe hemorrhoids should be treated with creams that contain hydrocortisone and witch hazel.
To remove a blood clot in an external hemorrhoid, the physician may use rubber band ligation. This involves placing rubber bands around the base of the internal hemorrhoids to cut off blood supply and force the hemorrhoid to wither.
Sclerotherapy is another minimally invasive procedure that involves injecting the hemorrhoid tissue with a chemical solution that forces the tissue to shrink.
Depending on the severity of the hemorrhoid, the physician may need to cut off the blood supply and/or cause scar tissue to form, helping to shrink the hemorrhoid. In other instances, patients may need a hemorrhoidectomy to remove large external hemorrhoids and prolapsing internal hemorrhoids.
Hemorrhoid stapling is another surgical procedure done to block blood flow to the hemorrhoidal tissue.






